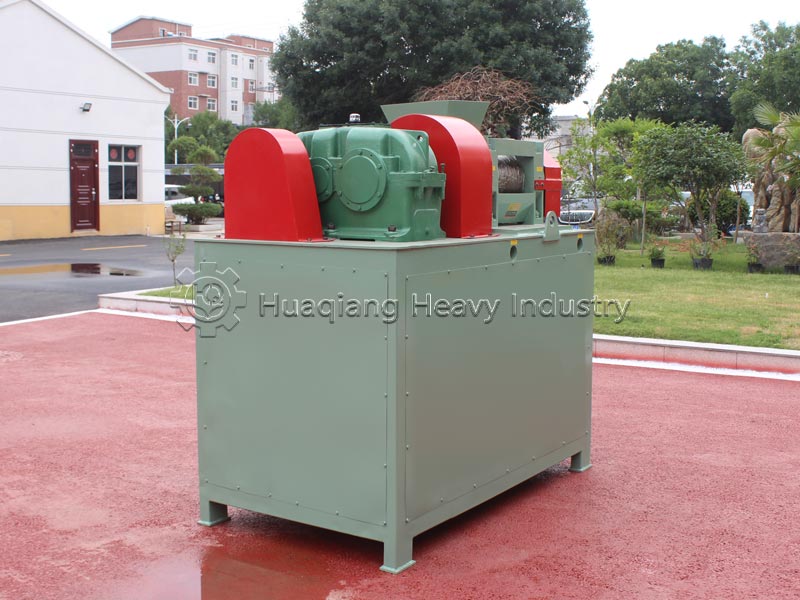
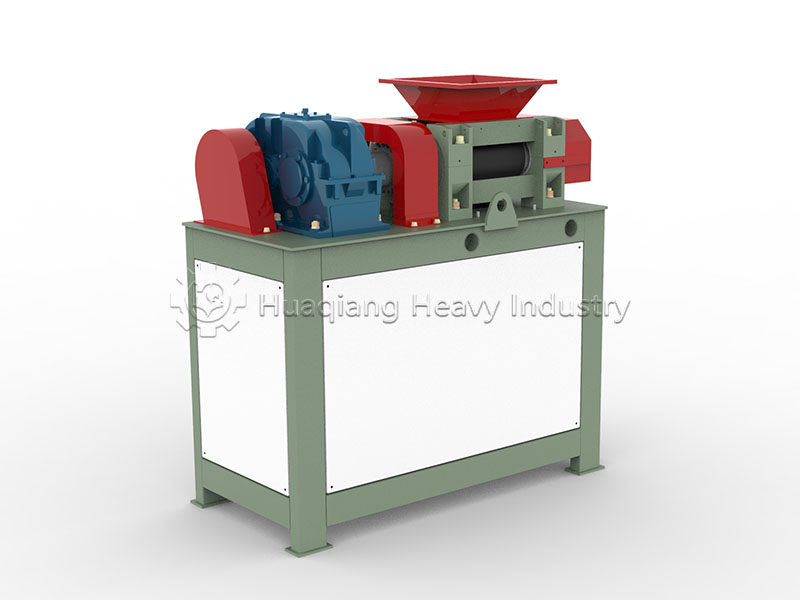
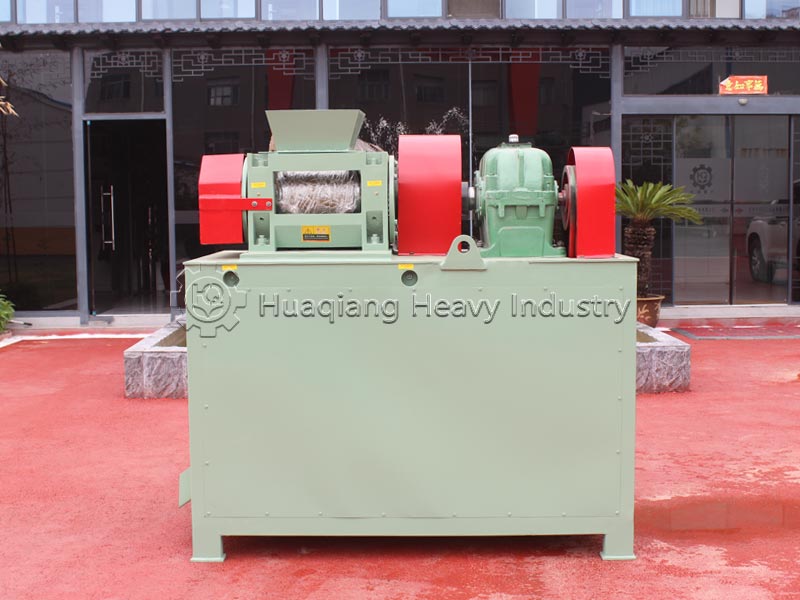
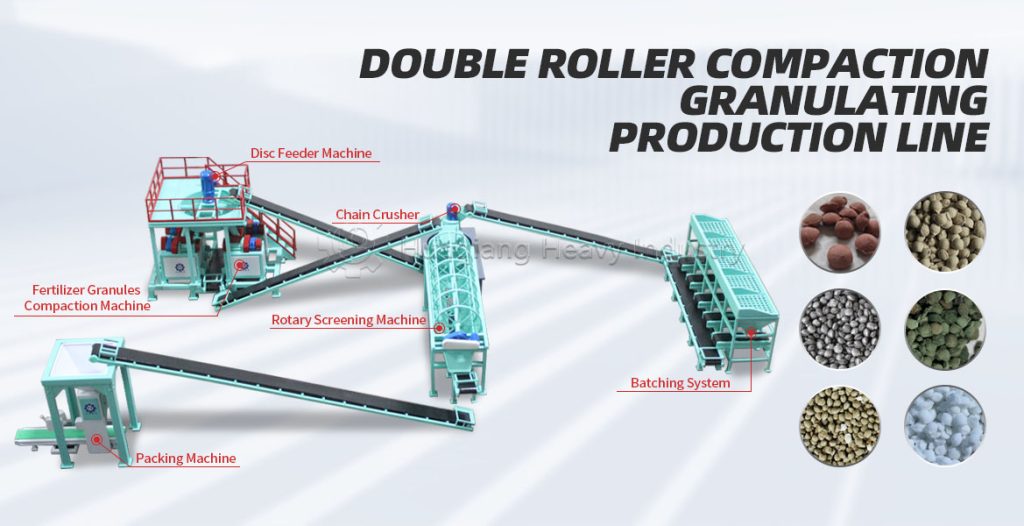
Double roller press granulators, with their advantages of dry granulation, no drying required, and low energy consumption, are commonly used equipment in fertilizer production lines. Achieving a high molding rate and stable particle strength is crucial, and this depends on controlling raw material suitability, parameter adjustment, and standardized operation.
Raw material pretreatment is fundamental. The moisture content of the raw materials should be controlled between 8% and 12%; too high a moisture content can lead to roller sticking and clumping, while too low a moisture content makes molding difficult. After crushing and screening, ensure the particle size is ≤2mm, and thoroughly mix the materials using a fertilizer mixer machine to avoid uneven composition. Coarse fiber and high-hardness raw materials need to be softened in advance to reduce the extrusion load.
Precise parameter adjustment is key. Adjust the roller gap (0.5-2mm) according to the target particle size; a gap that is too large results in loose particles, while a gap that is too small leads to high energy consumption and easy wear of the roller surface. Match the appropriate roller pressure and rotation speed according to the characteristics of the raw materials—increase the roller pressure and decrease the rotation speed for high-hardness materials, and vice versa for lightweight materials, ensuring a molding rate of ≥90%.
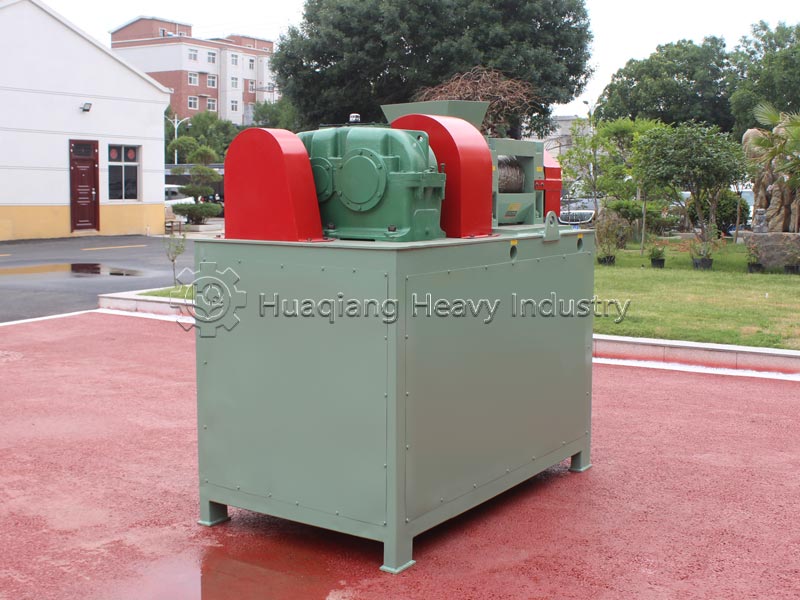

Standardized operation and maintenance are essential. Before starting, check the flatness of the roller surface and the lubrication of the transmission system to avoid idling wear; during operation, observe the particle morphology in real time and fine-tune the parameters; after shutdown, clean the residue on the roller surface, regularly polish the roller surface and tighten the connecting parts, and strictly prevent metal impurities from scratching the roller surface.
By mastering these techniques, you can fully utilize the advantages of the double roller press granulator, produce high-quality and stable fertilizer granules, extend equipment life, and adapt to various granulation needs such as NPK compound fertilizers, contributing to improved quality and efficiency in fertilizer production.