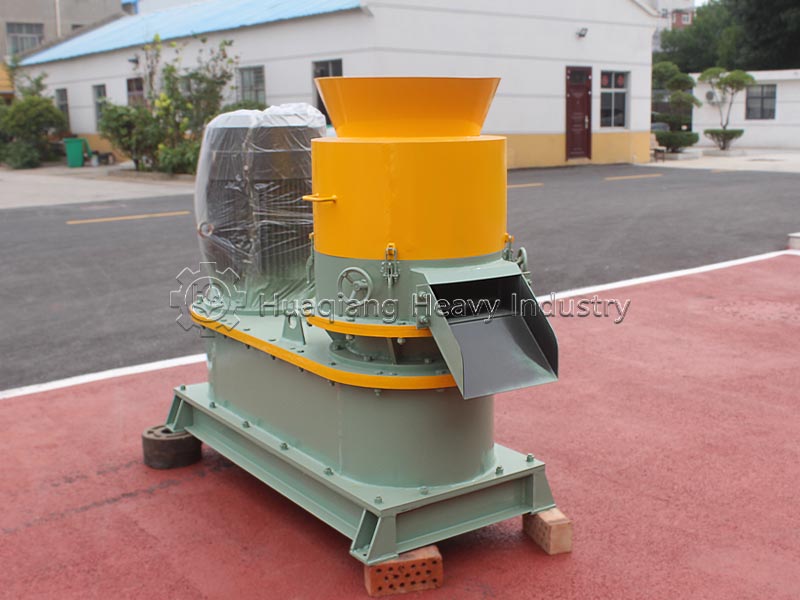
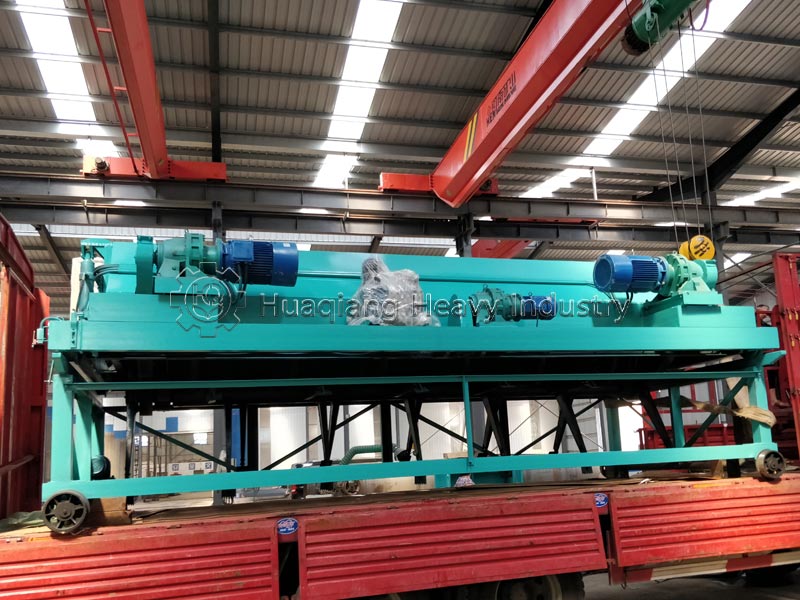
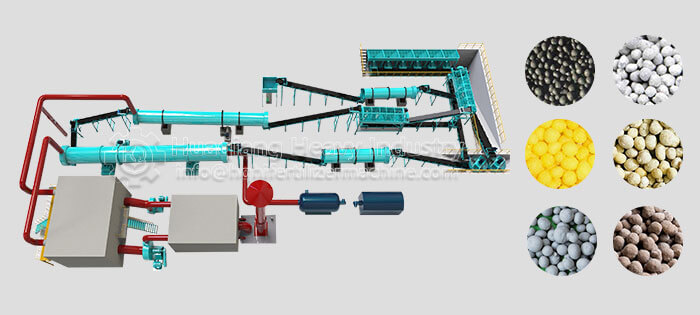
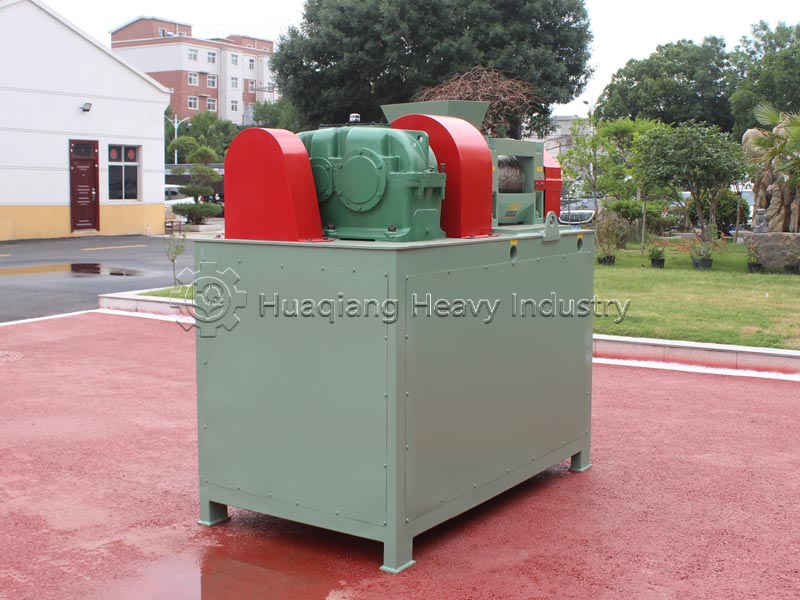
Potassium sulfate (SOP) is a high-quality, chlorine-free potassium fertilizer widely applicable to chlorine-sensitive crops such as tobacco and fruits and vegetables. However, its hygroscopic and highly crystalline properties place extremely high demands on the granulation process. Double roller press dry granulation technology, with its advantages of no drying, low energy consumption, and high purity retention, has become an ideal solution for potassium sulfate granulation.
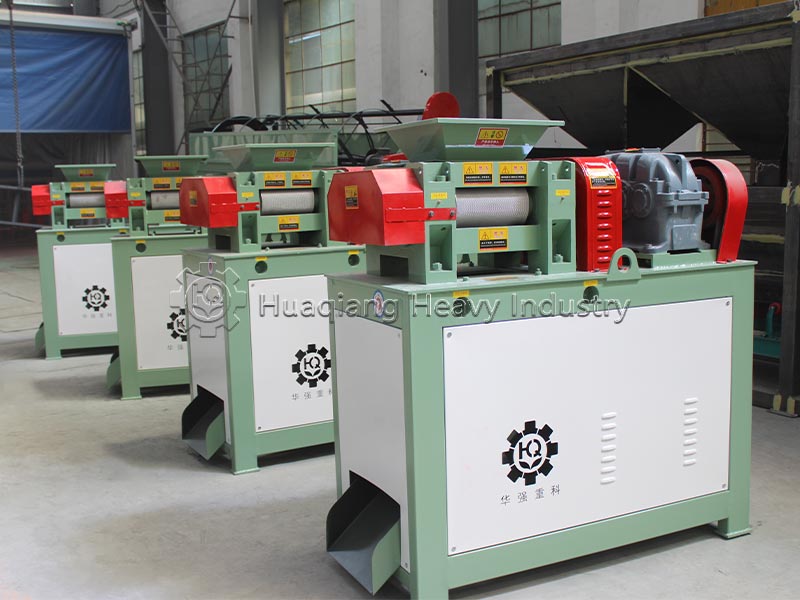
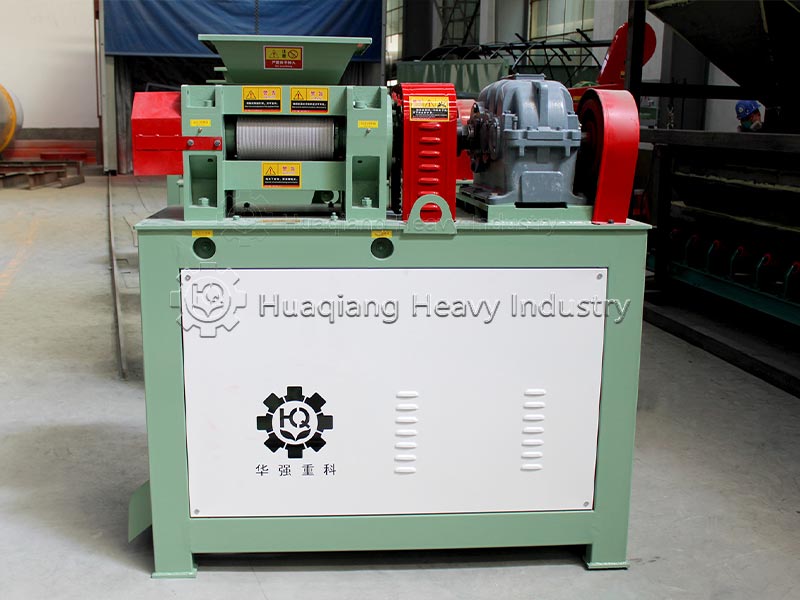
Potassium sulfate raw materials need to be screened by a fertilizer screener machine to remove impurities and dried at low temperature, controlling the moisture content to 2%-5% to prevent sticking to the roller surface during granulation. The double roller press granulator, by adjusting the 8-15MPa pressure and speed of the rollers, directly extrudes the dry powder into granules, requiring minimal binders, maximizing the preservation of SOP purity, and avoiding the moisture absorption and alkali return problems associated with wet granulation.

This process eliminates the need for high-temperature drying, reducing energy consumption by over 40%, and produces no wastewater or exhaust gas emissions, meeting environmental protection requirements. The granulated particles have a compressive strength ≥15N, uniform strength, and are not easily pulverized, making them suitable for mechanized fertilization and long-distance transportation, while also allowing for controllable dissolution rates.
The equipment can process potassium sulfate granules independently or be used in conjunction with a double axis paddle mixer to add micronutrients to create compound potassium sulfate fertilizer, flexibly adapting to different formulations. It is simple to operate and easy to change production lines, meeting the needs of large-scale production by large enterprises as well as batch processing by small and medium-sized workshops.
In summary, the double roller press granulator is precisely adapted to the characteristics of potassium sulfate, empowering the industrialization of potassium sulfate fertilizer and helping chlorine-sensitive crops to accurately supplement potassium, improve quality, and increase yield.