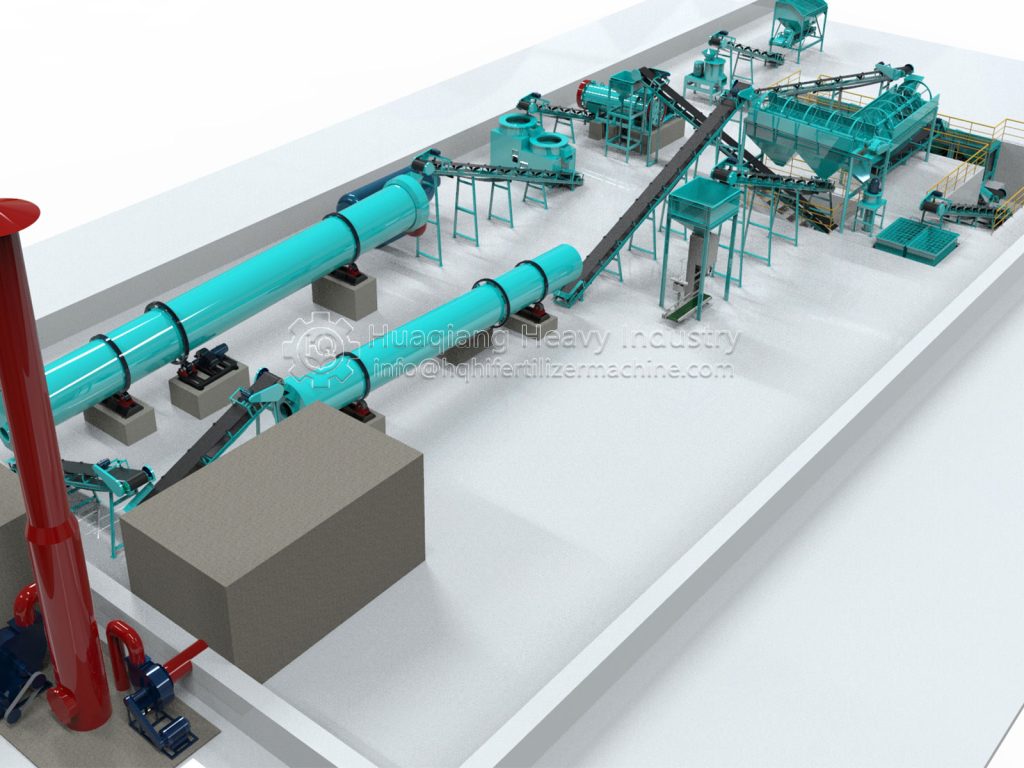
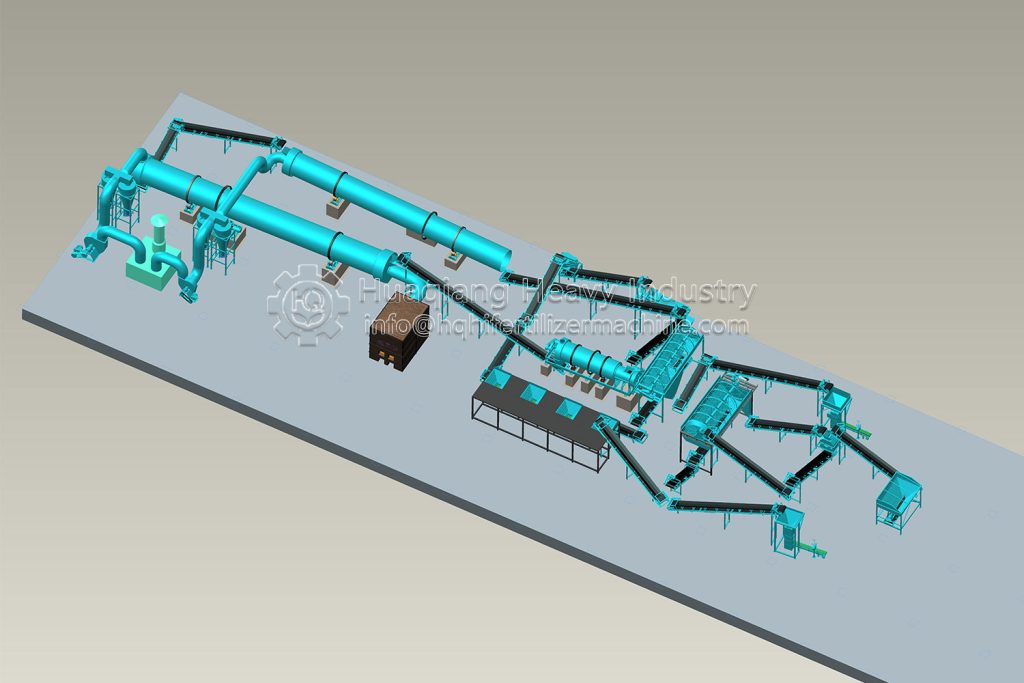
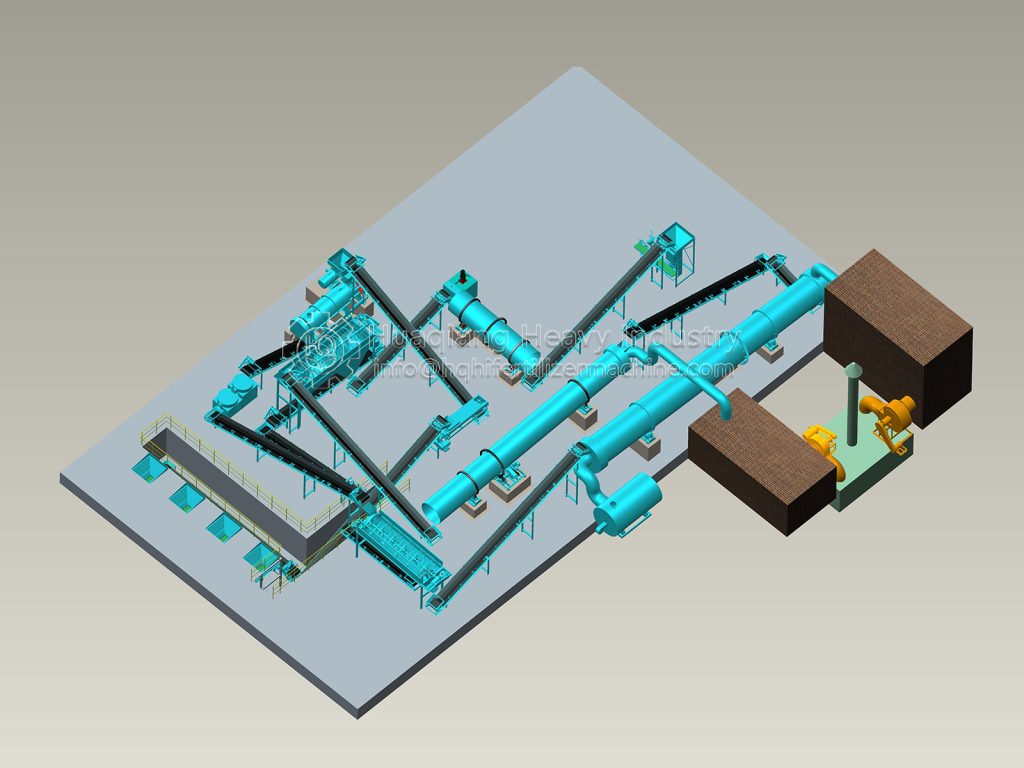
In organic fertilizer production lines, composting is a core step that determines the quality of organic fertilizer. Improper operation not only reduces fertilizer efficiency but can also lead to odor, pathogens, and other issues, impacting production efficiency and the environment. The following are key considerations during composting:

First, the raw material ratio must be scientifically and accurately formulated. Composting raw materials typically consist of livestock and poultry manure, straw, and mushroom residue. The carbon-nitrogen ratio (C/N) must be strictly controlled between 25:1 and 35:1. A high C/N ratio will slow composting and easily lead to a “cold pile.” A low C/N ratio will result in nitrogen loss and produce foul odors. Furthermore, the moisture content of the raw materials must be adjusted to 50%-60%. Hold the raw materials tightly with your fingers until water is present but not dripping. Excessive moisture can easily lead to anaerobic fermentation, while too low a moisture content can inhibit microbial activity.
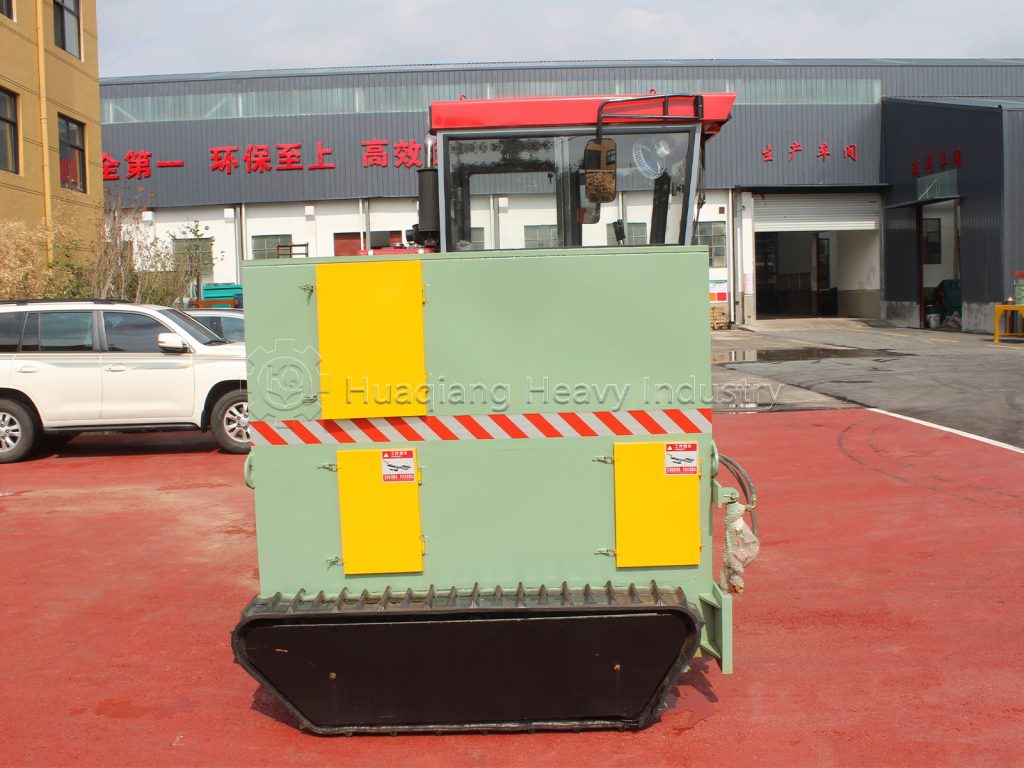
Second, compost management requires dynamic monitoring. The recommended height of the compost pile is 1.2-1.5 meters, and the width is 2-3 meters. The length should be adjusted according to the scale of the organic fertilizer production line. Excessively high or wide compost piles will result in poor ventilation, while excessively low compost piles will dissipate heat too quickly, making it difficult to maintain a high temperature. During the composting process, the compost should be turned regularly. Typically, the compost temperature should rise above 60°C for 2-3 days before being turned using a compost turner. This not only replenishes oxygen but also maintains a uniform temperature throughout the compost, helping to inactivate pathogens and weed seeds. The frequency of turning should be adjusted based on temperature fluctuations, generally once or twice a week.
Finally, environmental conditions must be strictly controlled. The composting room must maintain good ventilation to prevent the accumulation of harmful gases. Rain protection measures should also be implemented to prevent nutrient loss and water accumulation due to rainwater erosion. Furthermore, compost temperature and pH should be monitored in real time. During normal composting, the compost temperature should rise first, then fall, ultimately stabilizing at room temperature, with the pH maintained between 7.5 and 8.5. If abnormalities are detected, the raw material ratio or the turning frequency should be adjusted promptly. Only by strictly following these precautions can we ensure an efficient and stable composting process, produce high-quality organic fertilizer that meets standards, and provide strong support for the green development of agriculture.