The NPK blending fertilizer production line is the core of compound fertilizer production. The condition of its equipment directly affects product quality and production efficiency. Proper, science-based maintenance not only cuts unplanned downtime but also significantly extends equipment life and lowers production costs.
1.Raw Material Pretreatment System
Fertilizer crushers and screening equipment are the front-end critical units. Poor maintenance here causes problems later. Check hammer heads and screen mesh wear weekly. Replace them when wear reaches one-third of the original thickness. Clean out leftover material inside the equipment thoroughly after each day’s production to prevent caking and corrosion.
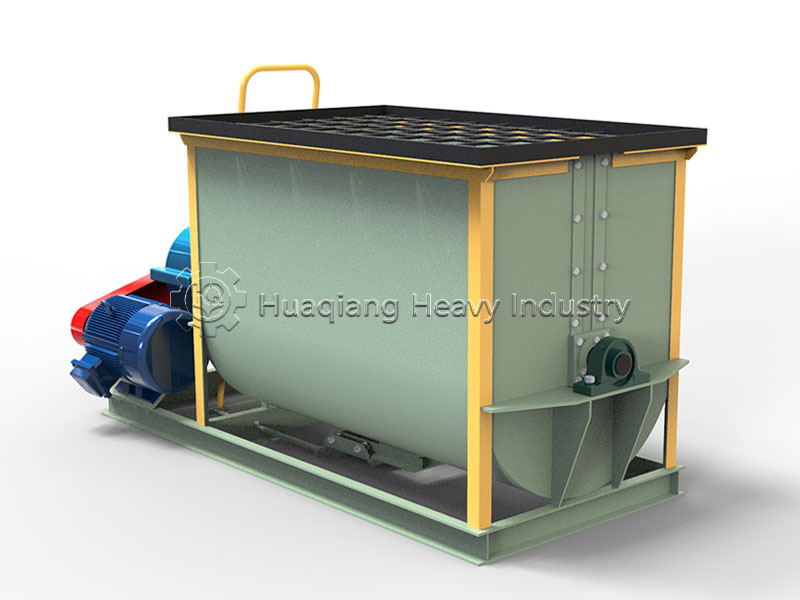
2.Mixing System
The double axis paddle mixer is the heart of blending. Pay special attention to paddle wear and shaft end seal condition. Measure the gap between paddles and the mixing chamber monthly. Adjust or replace paddles if the gap exceeds 5mm. Replace seals every six months to prevent lubricant leaks contaminating the product.

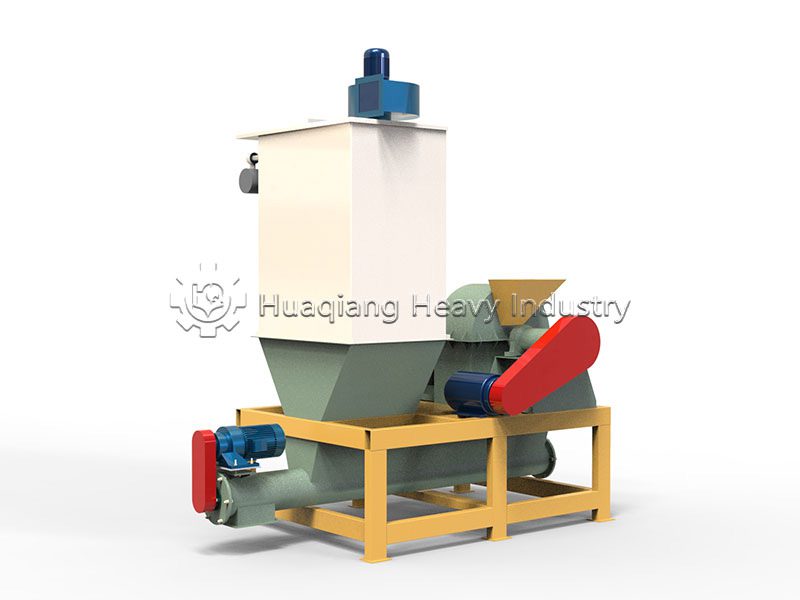
3.Packaging and Conveying Equipment
Automatic packing scales and belt conveyors directly impact packing accuracy and NPK blending fertilizer production line continuity. Calibrate packing scale sensors monthly using standard weights to keep weighing errors within ±0.2%. Check conveyor idler rollers quarterly for smooth rotation. Seized rollers significantly increase motor load.
Implementing these maintenance steps can greatly reduce equipment failure rates and boost the overall efficiency of the NPK blending fertilizer production line. This provides a solid foundation for stable product quality and controlled production costs.