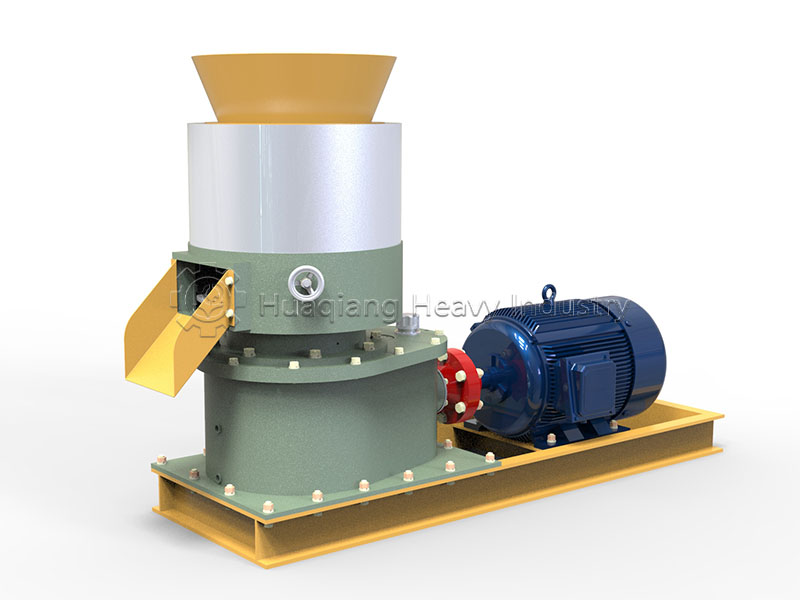
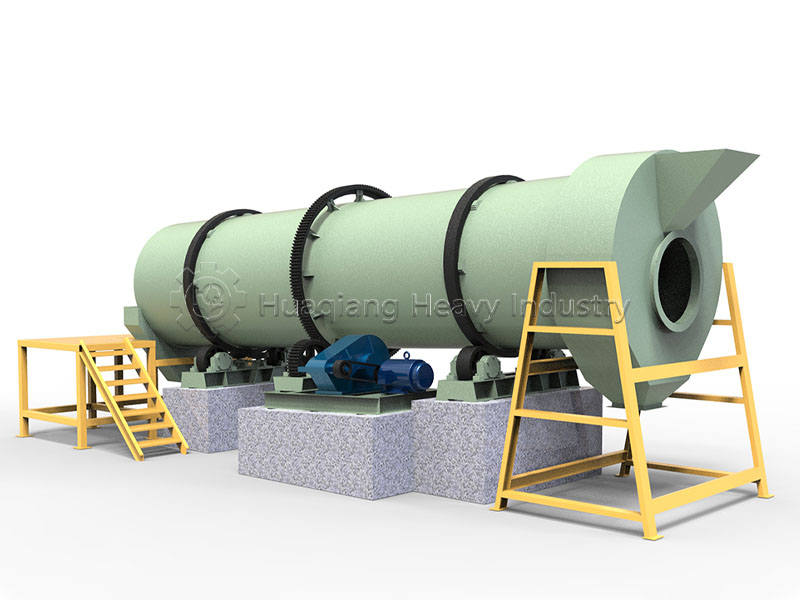
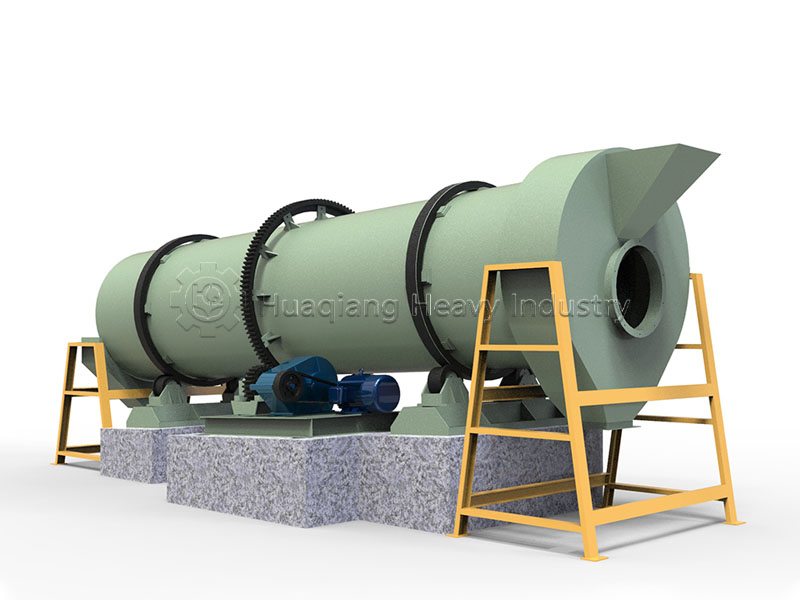
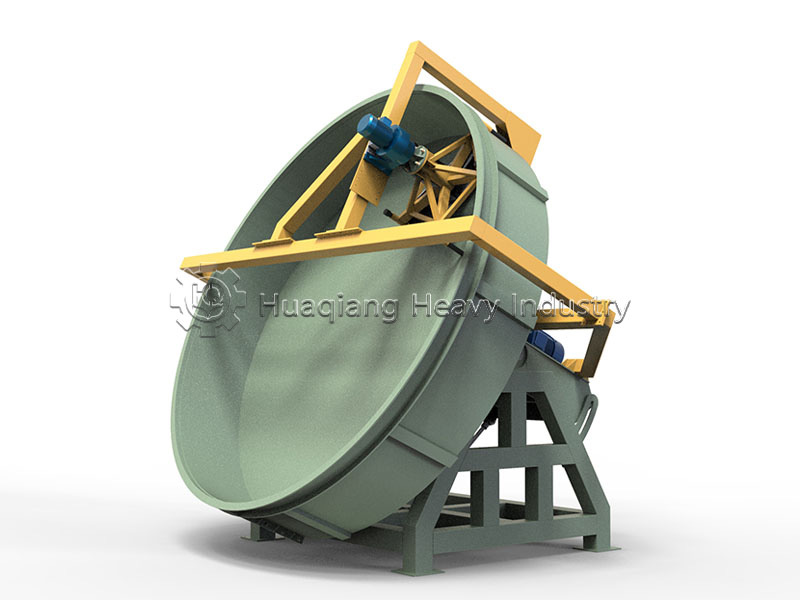
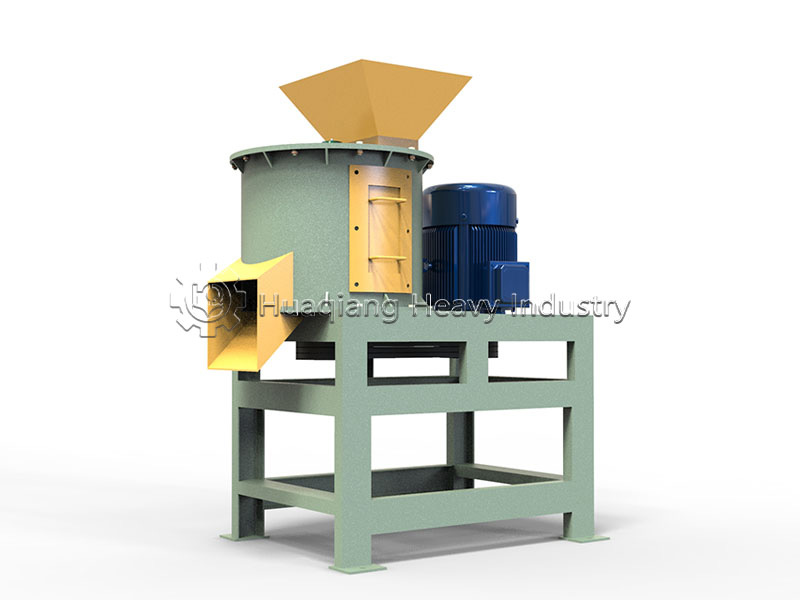
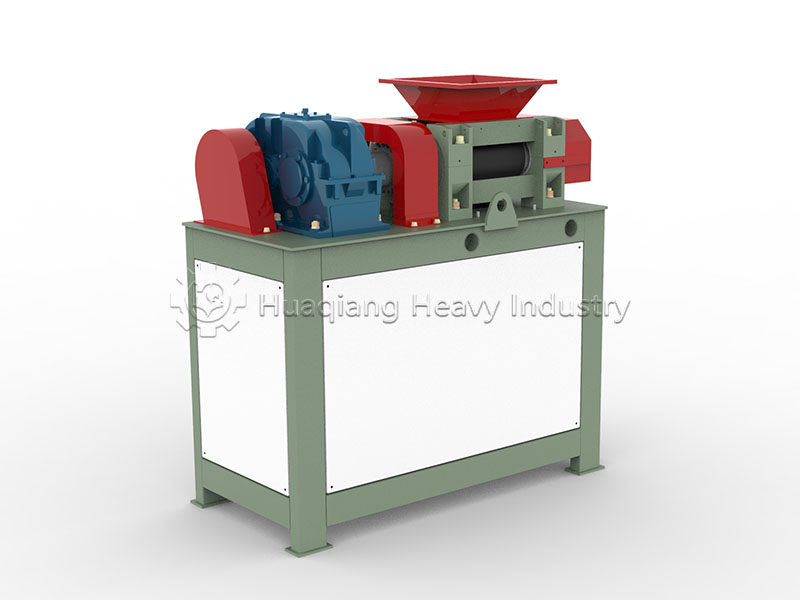
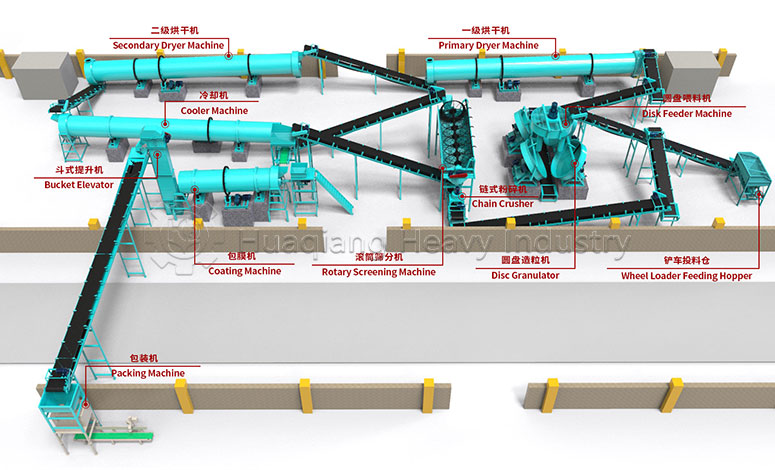
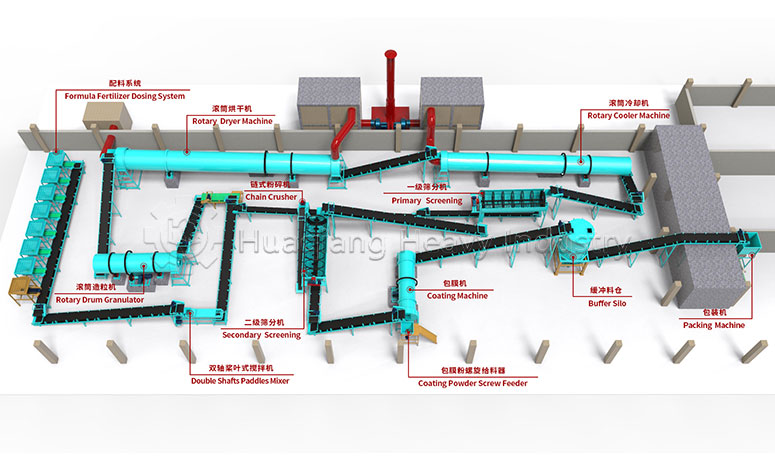
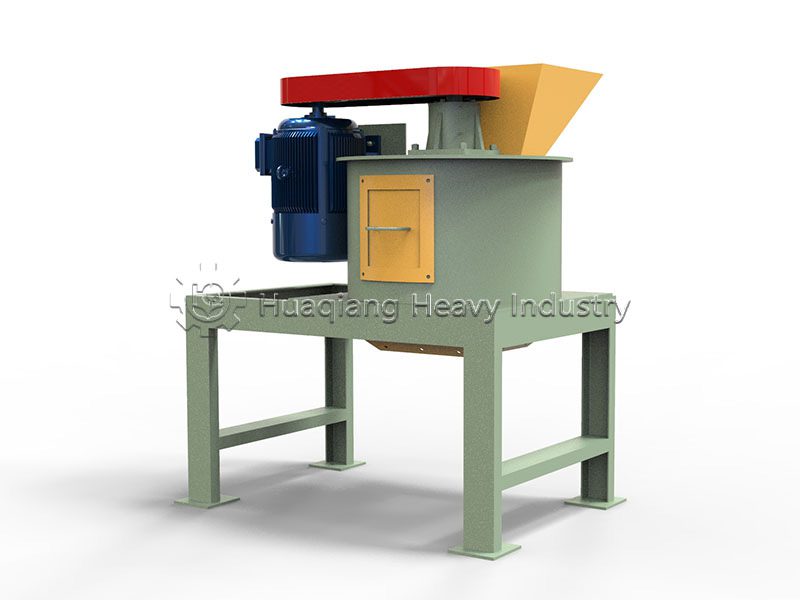
Under the trend of green agricultural development, the intelligent and efficient operation of bio-organic fertilizer production lines has become a goal pursued by the industry. As a key piece of equipment in bio-organic fertilizer production, the fertilizer crusher’s performance directly impacts the final quality and production efficiency of organic fertilizers. Whether for the reuse of agricultural waste or large-scale organic fertilizer production, it plays an irreplaceable and crucial role.
The fertilizer crusher boasts strong adaptability, capable of processing various raw materials such as straw, livestock and poultry manure, and composted materials, perfectly addressing the shortcomings of traditional crushing equipment in handling wet and mixed materials. In the bio-organic fertilizer production line, it connects the raw material pretreatment stage, crushing large raw materials into uniform particle sizes. This not only increases the contact area between the material and microorganisms, improving subsequent fermentation efficiency, but also lays a solid foundation for the subsequent granulation process, avoiding problems such as poor particle formation caused by uneven raw material particle size.

As one of the core pieces of bio-organic fertilizer equipment, it can be used in conjunction with chain crushers, horizontal crushers, and other equipment, flexibly adapting to different production needs such as bio-organic fertilizer production lines and NPK fertilizer production lines. By adjusting crushing parameters according to different raw material characteristics, it can precisely control the output particle size, meeting the production requirements of various fertilizer products such as powder fertilizers and granular fertilizers.
For organic fertilizer production enterprises, a high-quality fertilizer crusher not only improves the overall production capacity of the production line but also offers the advantages of convenient maintenance and low energy consumption, helping enterprises reduce production costs.