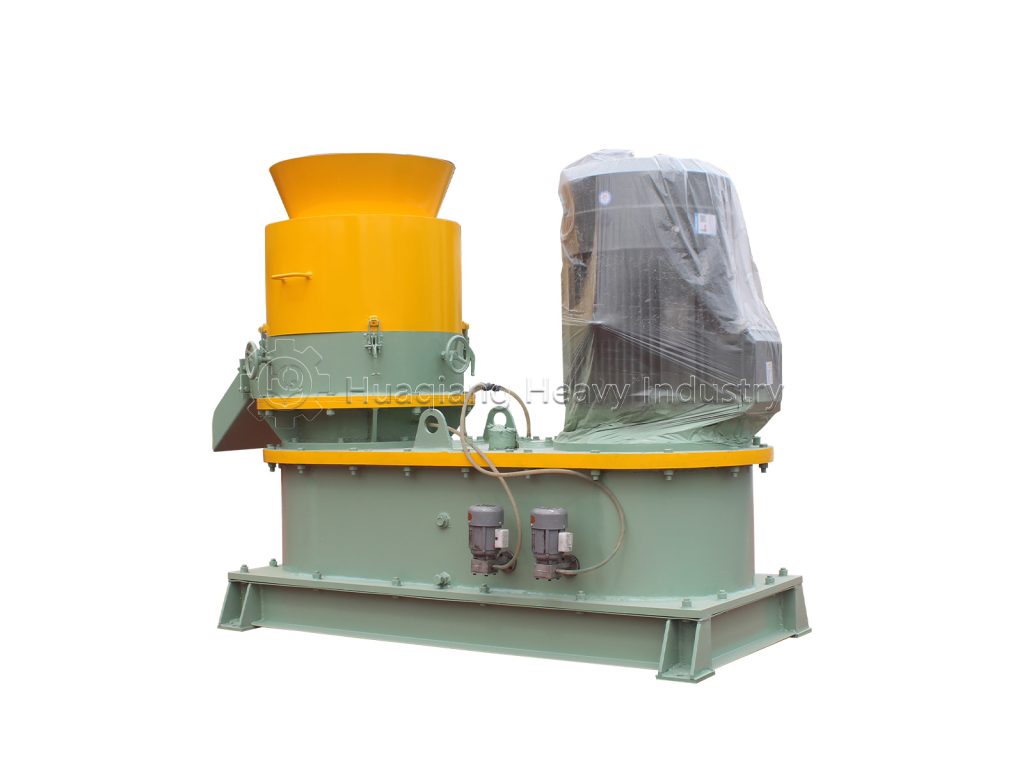
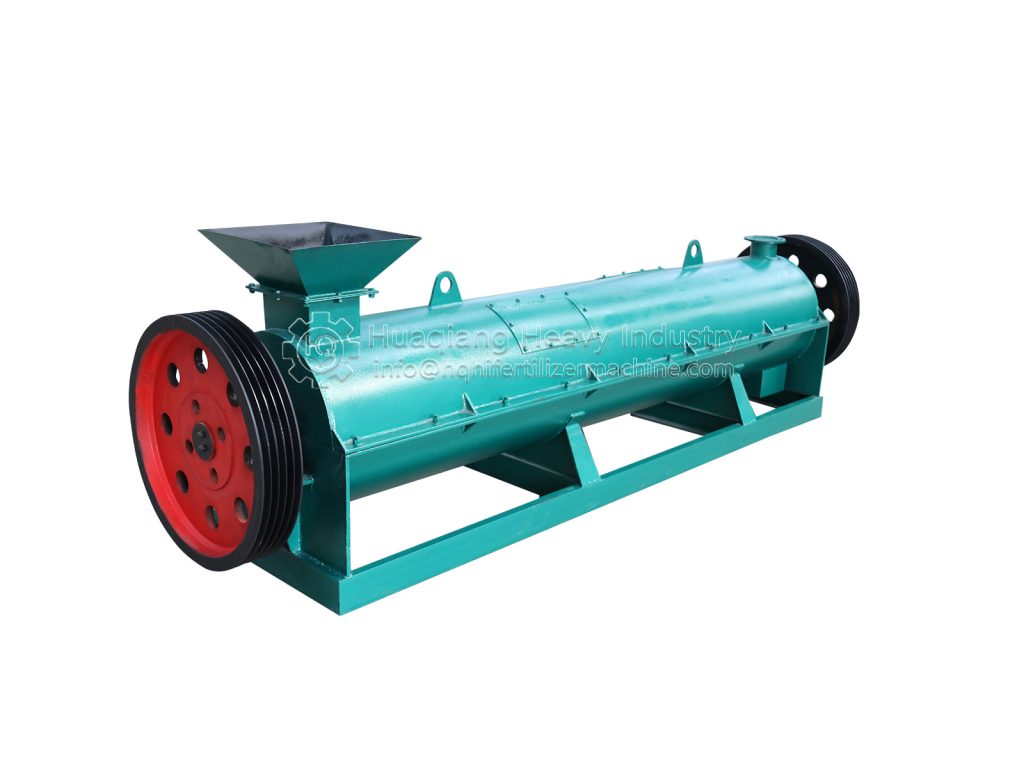
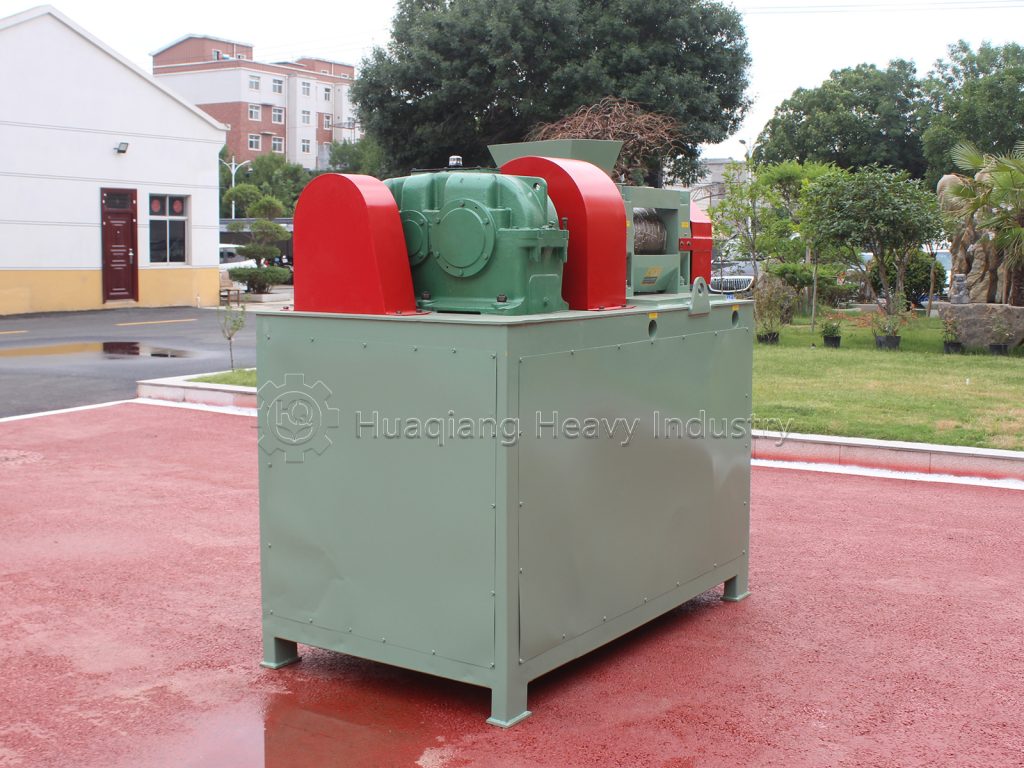
In organic fertilizer production, the granulator is a core piece of equipment that determines product quality and production efficiency. The flat die granulator, with its unique design, is the preferred equipment for organic fertilizer production lines. Its advantages are primarily reflected in five key areas.
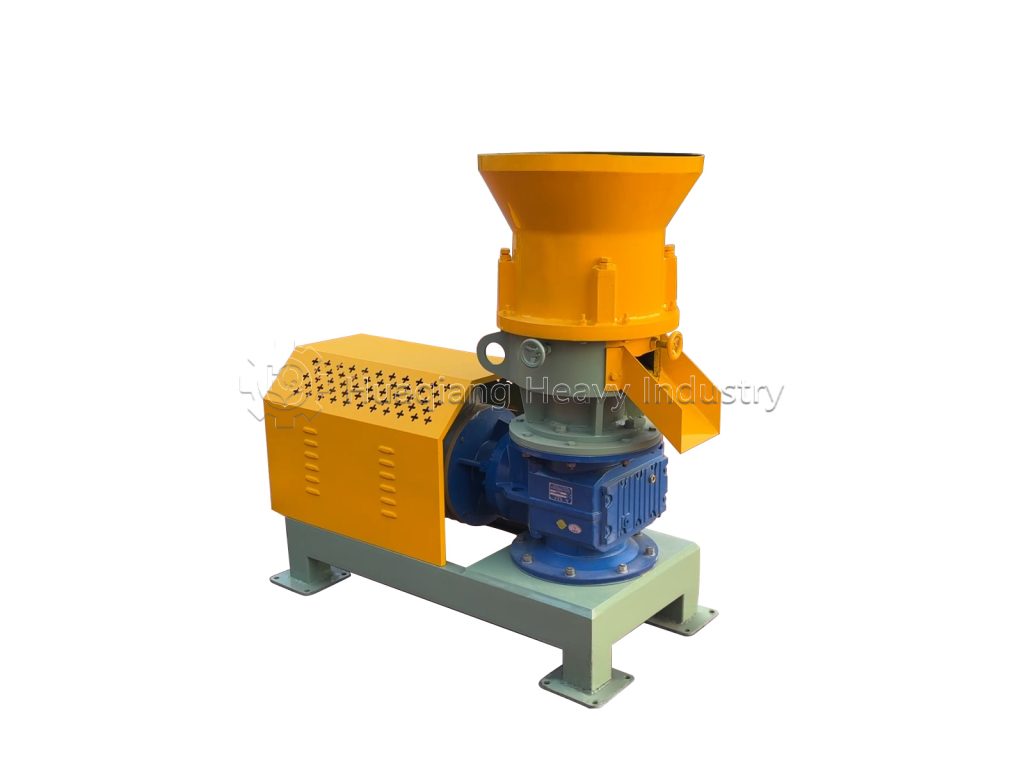

First, it offers excellent adaptability to raw materials. Organic fertilizer raw materials are complex, with common materials like livestock and poultry manure, straw, and mushroom residue exhibiting widely varying moisture and fiber content. By adjusting the pressure of the rollers and the speed of the die, the flat die granulator can easily process raw materials with a moisture content of 15%-30%. This eliminates the need for over-drying or the addition of large amounts of binders, preserving the beneficial microorganisms in the raw materials while reducing pretreatment costs. This makes it particularly suitable for the diverse raw material production needs of small and medium-sized organic fertilizer plants.
Second, the granulation quality is stable and controllable. The flat die granulator utilizes a “fixed die plate, rotating pressure roller” extrusion granulation method, achieving a pellet forming rate exceeding 95%. Pellet diameter can be flexibly adjusted (typically between 2 and 12 mm) by replacing dies with different apertures, meeting the pellet specification requirements for various applications, such as seedling fertilizer and field fertilizer. The pellets have a moderate hardness and are resistant to breakage, making them easy to package, transport, and spread in the field, effectively enhancing the product’s market competitiveness.
Furthermore, they offer low energy consumption and operating costs. Compared to ring die granulators, flat die pelletizers utilize a lower motor power, reducing power consumption by 20%-30% at the same production capacity. Furthermore, their consumable parts (such as the pressure roller and die) are made of wear-resistant alloy, offering a service life of over 3,000 hours. Replacement frequency is low, and the cost of spare parts is only half that of ring die pelletizers, significantly reducing production line operating expenses over the long term.
Furthermore, they are easy to operate and maintain. The flat die granulator boasts a simple and compact structure, a small footprint, and a quick installation and commissioning cycle. Operators can easily master the machine after minimal training. Routine maintenance requires only the regular addition of lubricating oil and cleaning of residual material from the die holes, eliminating the need for complex technical expertise. This significantly reduces labor costs and is particularly suitable for small and medium-sized manufacturers facing a shortage of skilled personnel.
Overall, the flat die granulator, with its high adaptability, cost-effectiveness, and ease of operation, is an ideal choice for improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring quality in organic fertilizer production lines. It provides strong support for the development of small and medium-sized organic fertilizer manufacturers.