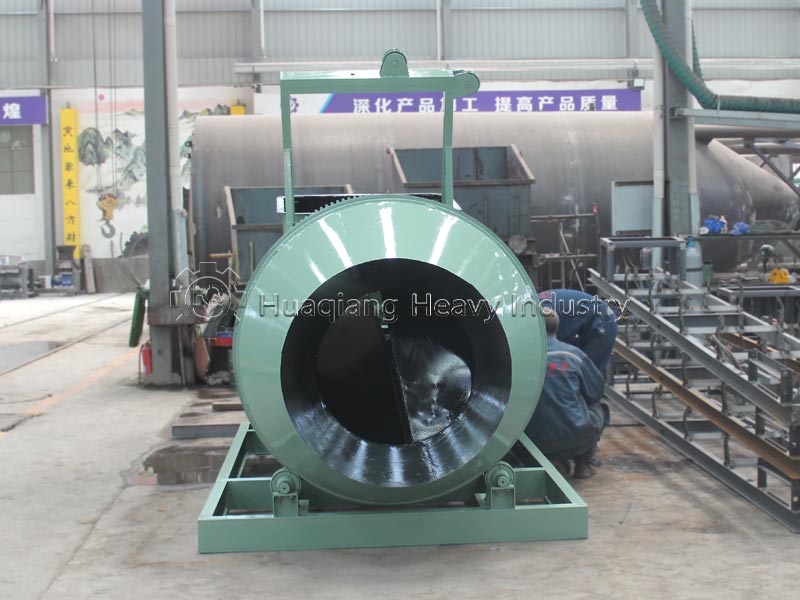
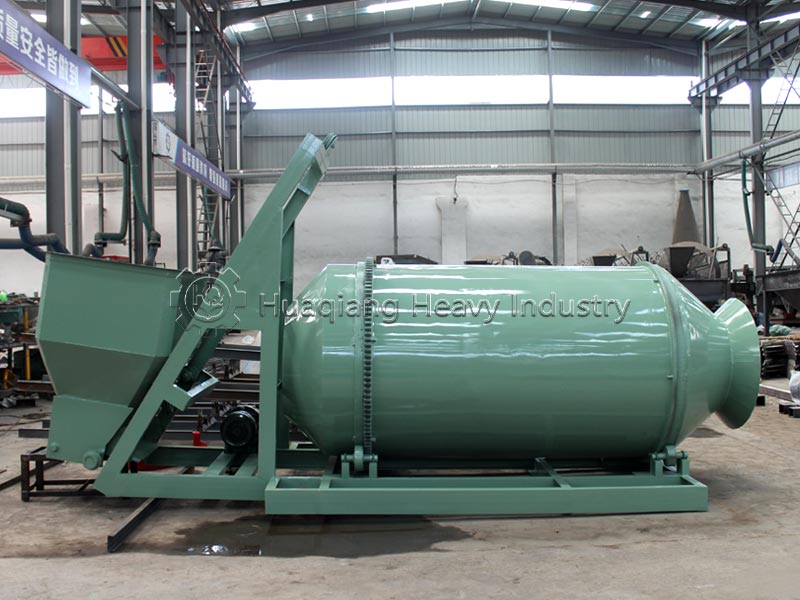
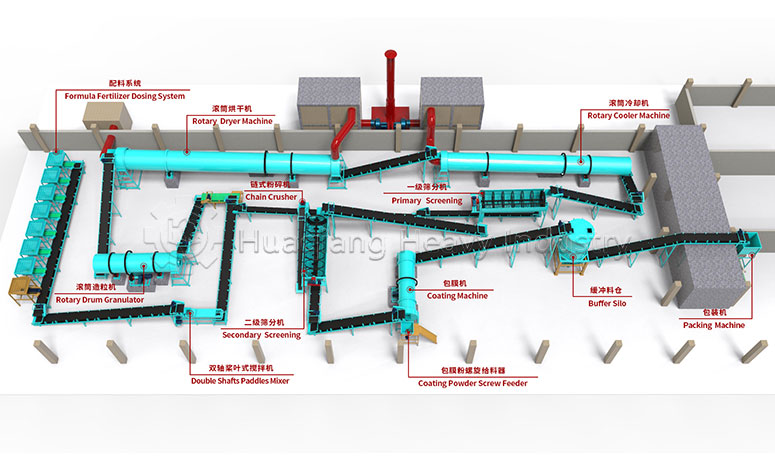
Against the backdrop of green transformation in agriculture, the market demand for balanced fertilizers has shifted from “general-purpose” to “precisely tailored,” with the core requirement being a precise match between nutrient ratios and soil and crop needs, while also accommodating flexible production of small batches and multiple formulations. The NPK blending fertilizer production line, with its unique technical characteristics, has become a core vehicle for meeting this demand.
Precise Proportional Mixing Capability: The key to balanced fertilizers is the balance of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and micronutrients. The automatic precision batching system of the NPK blending fertilizer production line can achieve a mixing accuracy of 0.1%, producing not only general formulas such as 15-15-15, but also customized formulas based on soil test data, such as high-potassium balanced fertilizers for potassium-deficient orchards.

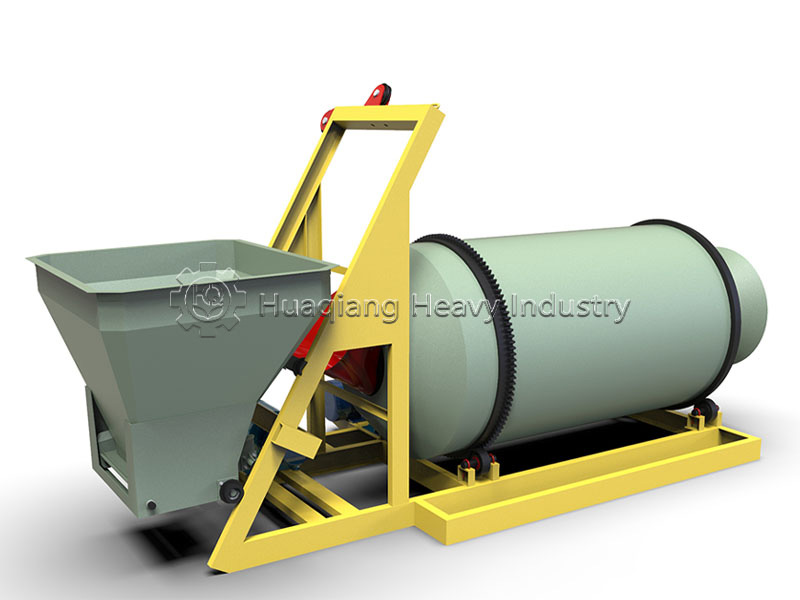
Adaptability to Diversified Needs: Currently, large-scale farms and scattered smallholder farmers coexist, resulting in significant differences in the demand for balanced fertilizers. The NPK blending fertilizer production line can flexibly switch formulas and can handle small batch orders as low as 10 tons, meeting the concentrated fertilizer needs of large cooperatives and also accommodating personalized orders from individual farmers.
Efficient Collaborative Capability: The production line uses a double axis paddle mixer or a BB fertilizer mixer to achieve uniform mixing of raw materials, avoiding nutrient imbalance. Combined with subsequent screening and testing processes, it ensures uniform granule size and nutrient content of the finished product. Its simplified process and rapid commissioning advantages allow it to quickly respond to the demand for new types of balanced fertilizers.
In summary, the NPK blending fertilizer production line, with its core advantages of precise proportioning, flexible production, and efficient collaboration, can fully meet the diversified and precise needs of the market for balanced fertilizers.