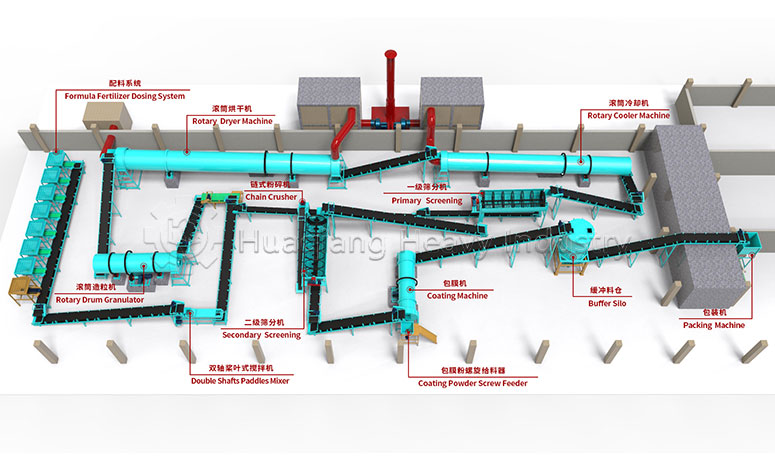
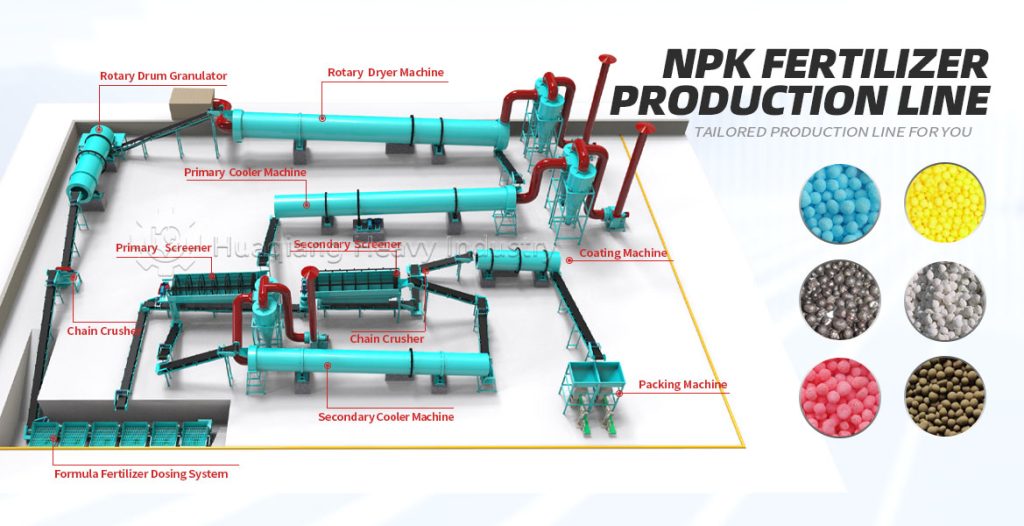
A high-efficiency, stable organic fertilizer production line begins with the meticulous pretreatment of raw materials. While the crushing stage is at the forefront of the entire organic fertilizer production equipment system, it fundamentally determines the quality of subsequent fermentation and the finished product.
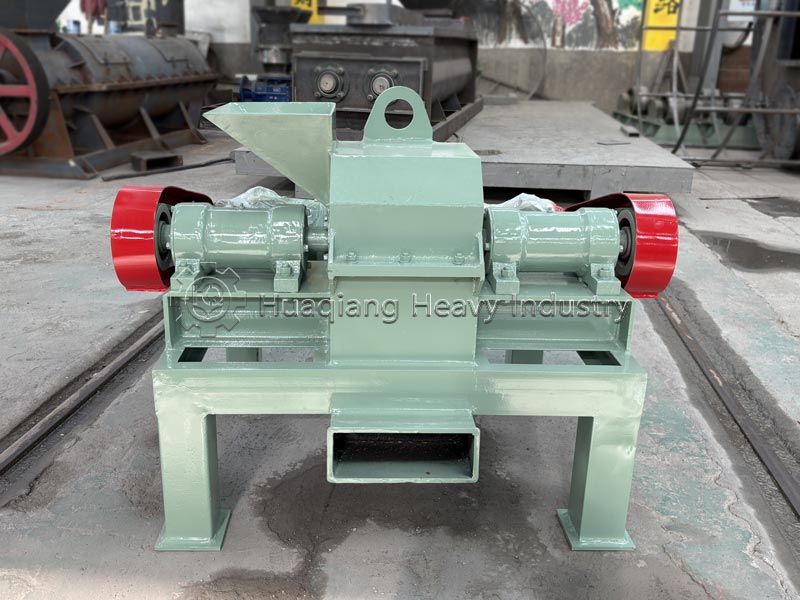
Among these processes, the half-wet material crusher demonstrates a unique advantage in handling high-moisture raw materials. It effectively crushes sticky and moist materials such as fresh poultry and livestock manure, kitchen waste, and straw, solving the pain points of traditional crushers, such as easy clogging and low efficiency. Its special anti-stick design ensures that even high-moisture materials can be smoothly broken up, creating ideal physical conditions for subsequent uniform fermentation and rapid decomposition. This is a key link in improving the adaptability of raw materials in modern organic fertilizer production lines.
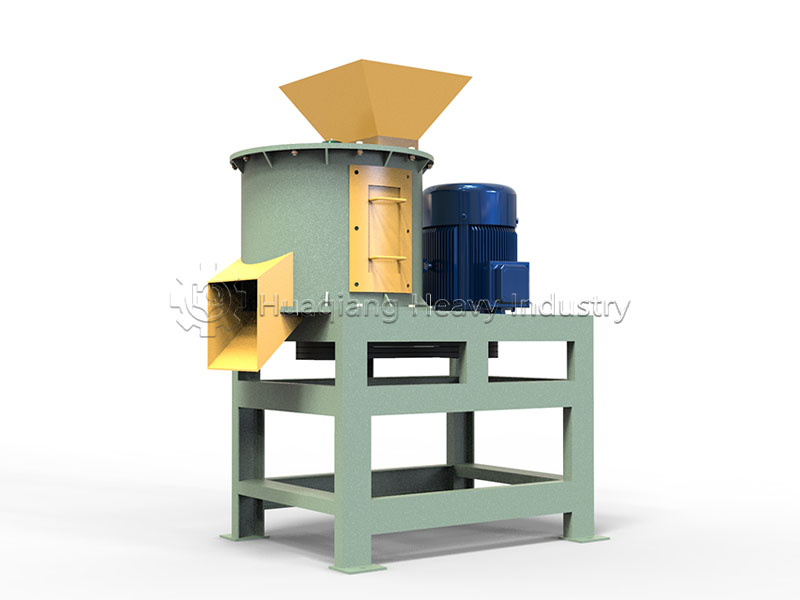

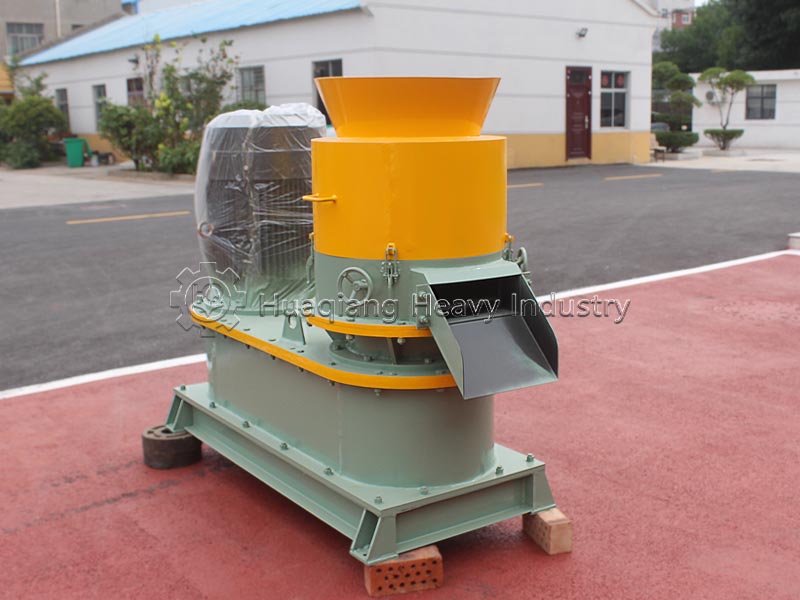
From the “coarse crushing” of raw waste by the half-wet material crusher to the “fine crushing” of fermented materials by the fertilizer crusher, these two types of equipment form a highly efficient pretreatment combination at the forefront of the organic fertilizer production line. Together, they transform raw materials of varying shapes and moisture levels into materials of uniform specifications that are easy to process, ensuring the smooth operation of the entire production line and the stable quality of the final product.
Therefore, when constructing a complete organic fertilizer production equipment system, paying attention to the crushing process and investing in specialized equipment are indispensable steps to achieve the resource utilization, large-scale, and high-value utilization of organic waste.